Bypassing CORS errors in development

Have you also been left frustrated at some point in development when you are expecting a response from an API but get stuck due to a CORS error? It’s one of those frustrating moments where you want to proceed but the errors continuously hold you back. While working with APIs in your application’s code, many times API fails and we get this error in the console.

In this blog, we explain in detail how to bypass the CORS errors in development.
Background
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS):
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a browser mechanism that enables controlled access to resources from a different origin. It explicitly allows some cross-origin requests while rejecting the others, hence adding flexibility to the same-origin policy (SOP).
SOP (same-origin-policy):
When you request a resource from an application of a different origin, the web browser uses an SOP (same-origin policy) protocol to block all your requests to that origin.
What does origin mean:
Origin is a combination of the scheme (or protocol, eg, HTTP or HTTPS), hostname (eg, example.com), and port (if specified, eg. 8080).
As client and server are separate applications, they are usually hosted on different domains. For instance, if our frontend is running on (http://localhost:3000) and the API we want to fetch data/server is running on (http://localhost:8080) since they live under different domains, the browser applies the same-origin policy and blocks any request going from the former to the latter.
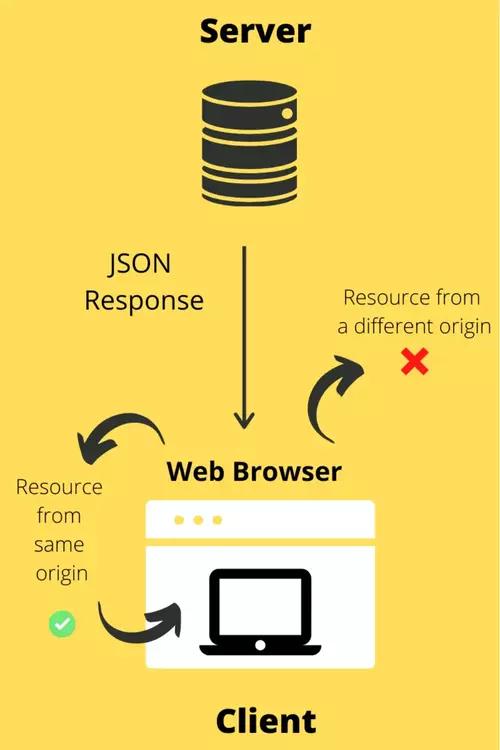
SOPs were necessary to ensure that any malicious website, say facebooook.com, cannot access your private data from Facebook.com. However, this underlying security rule governing browsers does not allow you to request a resource from a different origin. That's a common use case widely used across web apps today. CORS comes into the picture to enable you to access resources from different origins.
CORS Errors:
For security reasons, browsers restrict cross-origin HTTP requests initiated from scripts. For example, XMLHttpRequest and the Fetch API follow the same-origin policy. This means that a web application using those APIs can only request resources from the same origin the application was loaded from unless the response from other origins includes the right CORS headers.
If the CORS configuration isn't setup correctly, the browser console will present an error indicating that the request was blocked due to a violation of CORS security rules something like
"Cross-Origin Request Blocked: The Same Origin Policy disallows reading the remote resource at $somesite"
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS/Errors contains a couple of CORS errors as per the MDN doc.
Error Fixes
Although CORS exists for security reasons, when developing locally, CORS errors can be a pain. This guide contains some solutions that can be used for disabling CORS locally (and therefore fixing any CORS errors whilst developing your app locally).
Supporting CORS locally by Proxying API Requests in Development
What is Proxy server: It acts as a channel between client and server. When you make a request to a server, it is routed through the proxy, which receives the response from the server and transmits the information back to the client.
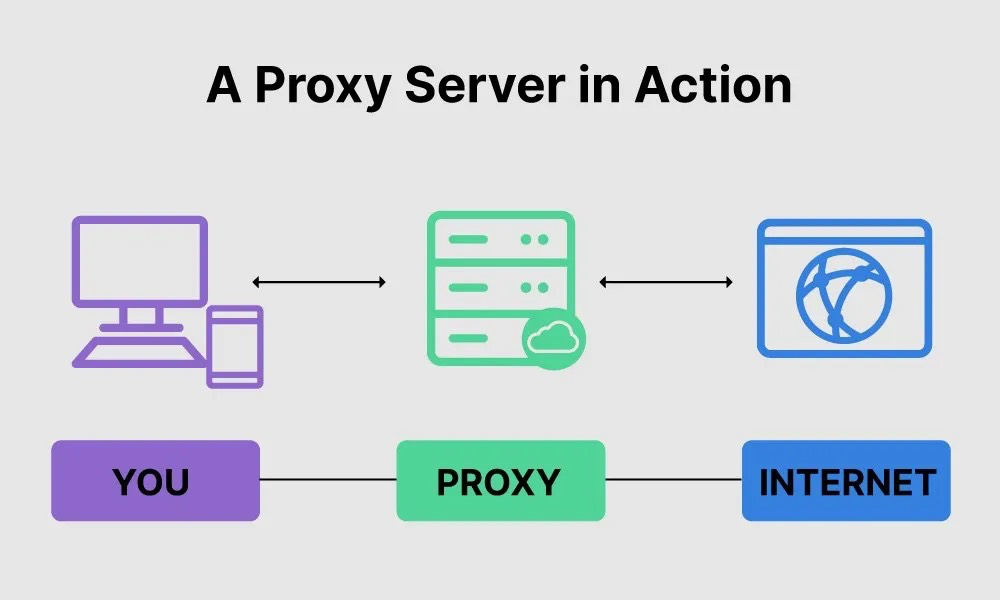
How to Proxy to backend server:
1. Use the default Create React App proxy:
To tell the development server to proxy any unknown requests to your API server in development, add a proxy field to your package.json like,
Eg, “proxy”: “https://randomservice.com”
Example to demonstrate setup of Proxy Server in React -
1. create-react-app setup:
1npx create-react-app react-cors-guide
2. Edit App.js file and include the following code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20import React, { useEffect } from ‘react' const App = () => { useEffect(() => { fetch('https://mojapp.in/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); }, []) return ( <div>------- CORS erros fix ----------</div> ) } export default App;
The fetch function is used to make API request to a cross-origin URL ‘https://mojapp.in/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm'
3. Now to start the application run:
1 2cd react-cors-guide npm start
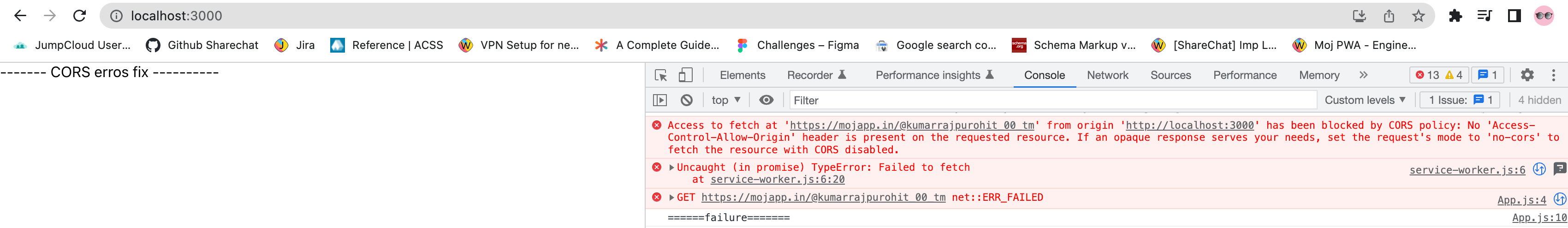
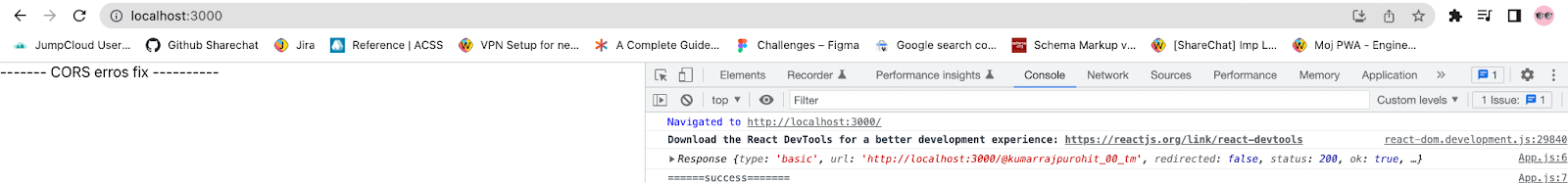
By default, the application should be running on ‘localhost:3000’. Below is the attached info with CORS error shown in console.
4. To fix this issue we’ll define our CRA’s default proxy.
- Include a ‘proxy’ field in package.json file:
1"proxy": "https://mojapp.in"
- Modify fetch request URL by removing origin in App.js and change to
/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm
5. By doing so we removed the different origin and structured the request URL as if it were a same-origin request. This seems in line with browser's SOP, and you no longer get the CORS error. The request should be successful, as shown in the browser console. Since the response URL is transmitted to the browser as same-origin (i.e. http://localhost:3000/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm ) CORS error is removed.
How to proxy to multiple APIs:
We may also make requests to several servers by specifying the routes that should be used to target a specific domain. To accomplish this, we’ll structure our proxy field in the package.json file and App.js like so:
1. Add following lines of code in package.json file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10"proxy": { "/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm": { "target": "https://mojapp.in", "changeOrigin": true }, "/teams": { "target": "https://stackoverflow.co", "changeOrigin": true } }
2. Update App.js file with following code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29import React, { useEffect } from 'react' const App = () => { useEffect(() => { fetch('/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); fetch('/teams') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); }, []) return ( <div>------- CORS erros fix ----------</div> ) } export default App;
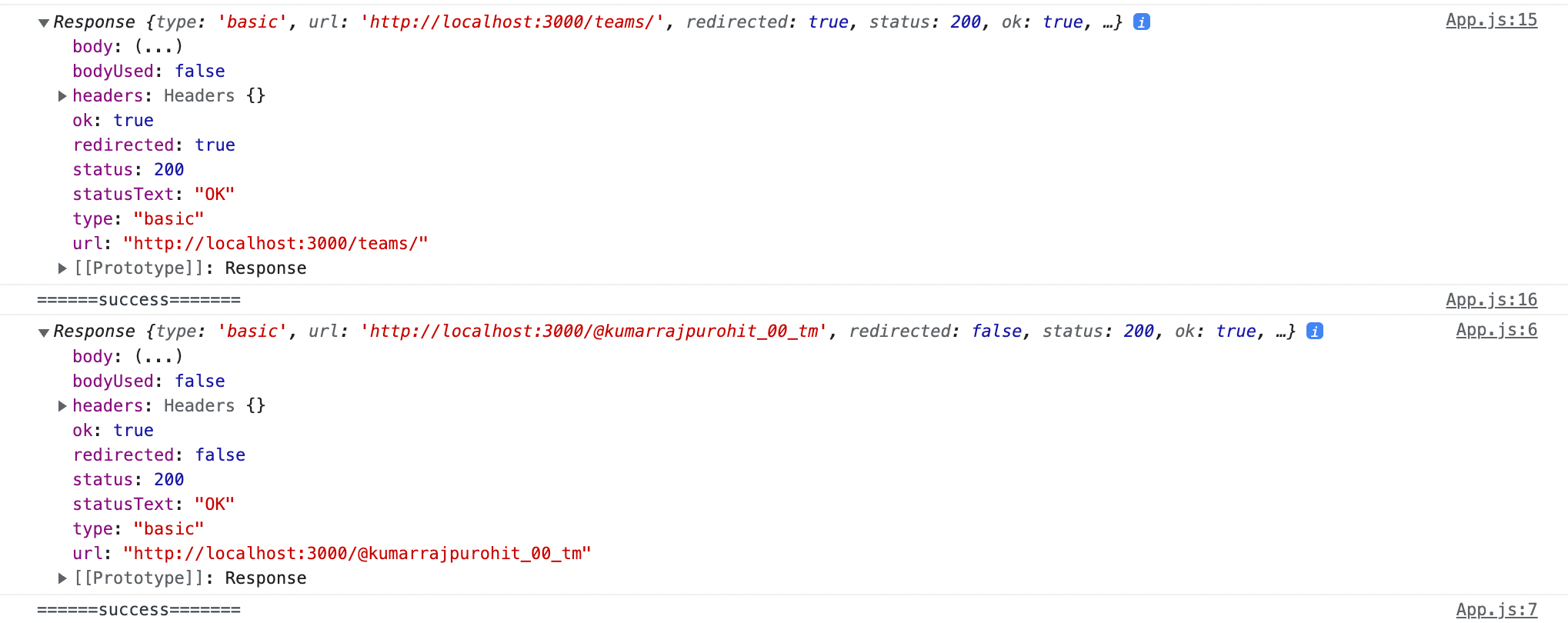
Browser console should look as in attachment below with no CORS errors:
2. Use a manually created proxy in Create React App:
One can use ‘http-proxy-middleware’ npm package to solve the CORS error issue.
NOTE- This feature is available in react-scripts@2.0.0 or higher.
Steps to Install This Package as a Project Dependency -
1. Open terminal and execute following command:
1npm i http-proxy-middleware —save
2. Create a new file named ‘setupProxy.js’ in the src directory. Add the following code snippet to the setupProxy file to register proxies:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8const { createProxyMiddleware } = require('http-proxy-middleware'); const proxy1 = { target: 'https://mojapp.in', changeOrigin: true }; const proxy2 = { target: 'https://stackoverflow.co', changeOrigin: true }; module.exports = function (app) { app.use('/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm', createProxyMiddleware(proxy1)); app.use('/teams', createProxyMiddleware(proxy2)); };
The code snippet above exports a function to the application so that the proxy middleware is registered to the application as soon as the development server starts up, without the need to import it into any file. Once the application is launched, it will start automatically.
3. Update App.js with following lines of code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38import React, { useEffect } from 'react' const App = () => { useEffect(() => { fetch('/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); fetch('/teams') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); fetch('https://stackoverflow.com/questions') .then(resp => { console.log(resp); console.log('======success======='); }) .catch(err => { console.log('======failure======='); console.log(err); }); }, []) return ( <div>------- CORS erros fix ----------</div> ) } export default App;
When you fetch (‘/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm'') and (‘/teams’) in development, the development server will recognise that it’s not a static asset, and will proxy your request to "http://localhost:3000/@kumarrajpurohit_00_tm'' and “ http://localhost:3000/teams'' as a fallback.
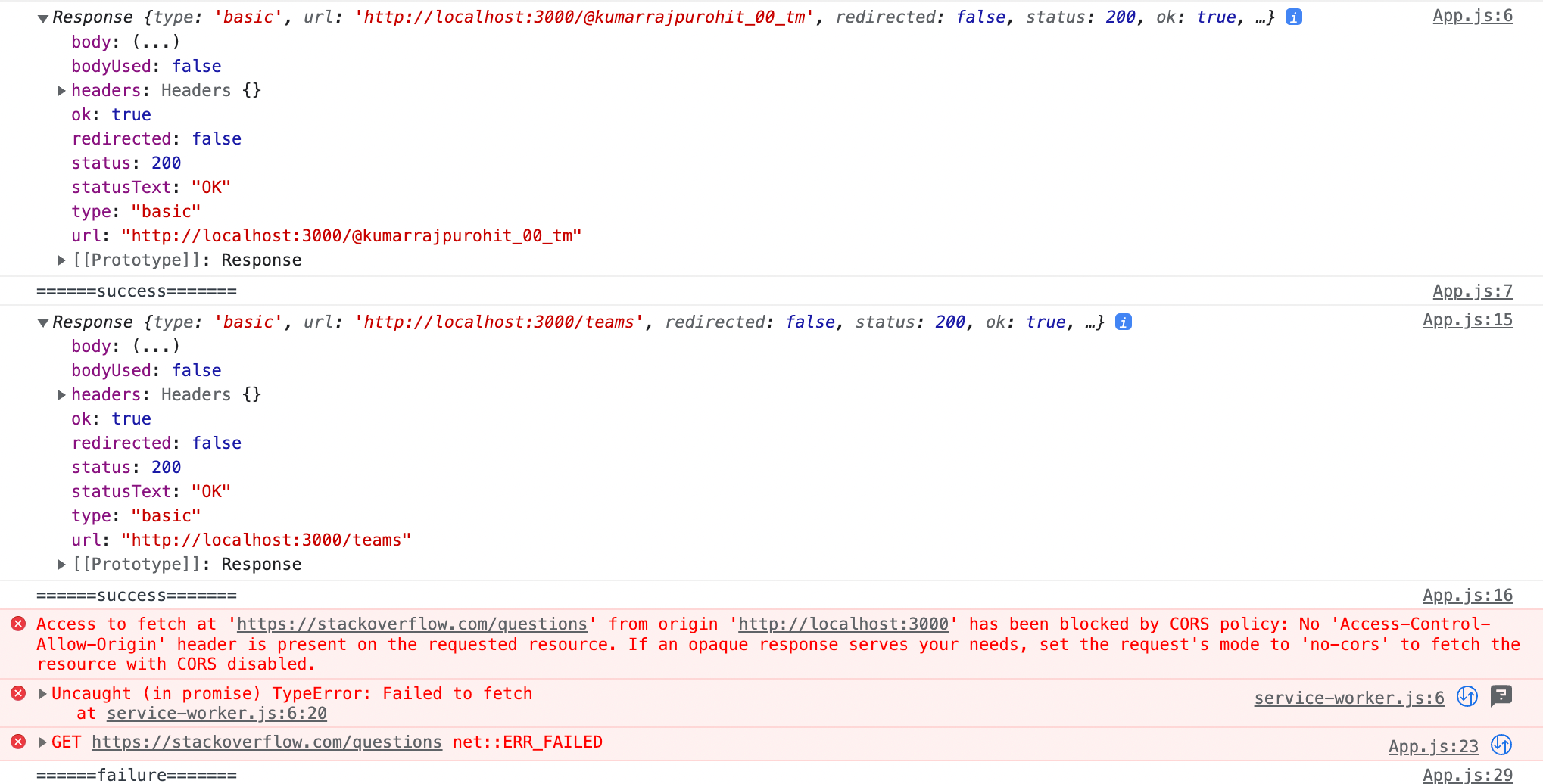
Hence origin is same, we won’t get a CORS error. But for the 3rd fetch request made to "https://stackoverflow.com/questions"since client and server origin are different CORS error will be thrown as in console attachment below.
Disable CORS in the browser:
One can directly disable CORS errors in the browser for different application following steps below:
Chrome
MAC
- Force quit Chrome by going to the mac menu and pressing “force quit” (or pressing command Q).
- Then run this command to open Chrome with web security disabled
1open -n -a /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome --args --user-data-dir="/tmp/chrome_dev_test" --disable-web-security
3. To enable web security again, force quitting chrome and restarting should enable security flags.
Windows
If you are using Windows, navigate to the path of your installation via a command prompt and run following command:
1Chrome.exe --disable-web-security
Firefox
One can install plugin like CORS Everywhere (https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/cors-everywhere/)
Below is a sample scenario where enabling CORS everywhere extension, we are able to disable CORS errors.
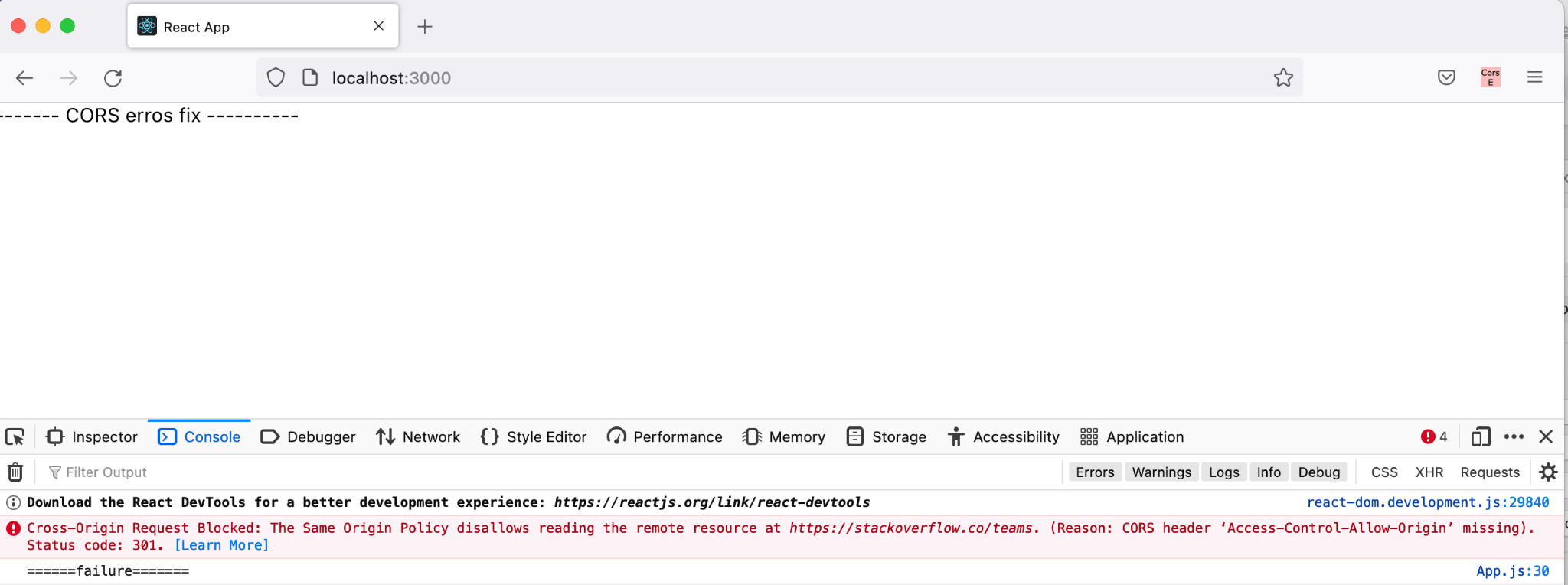
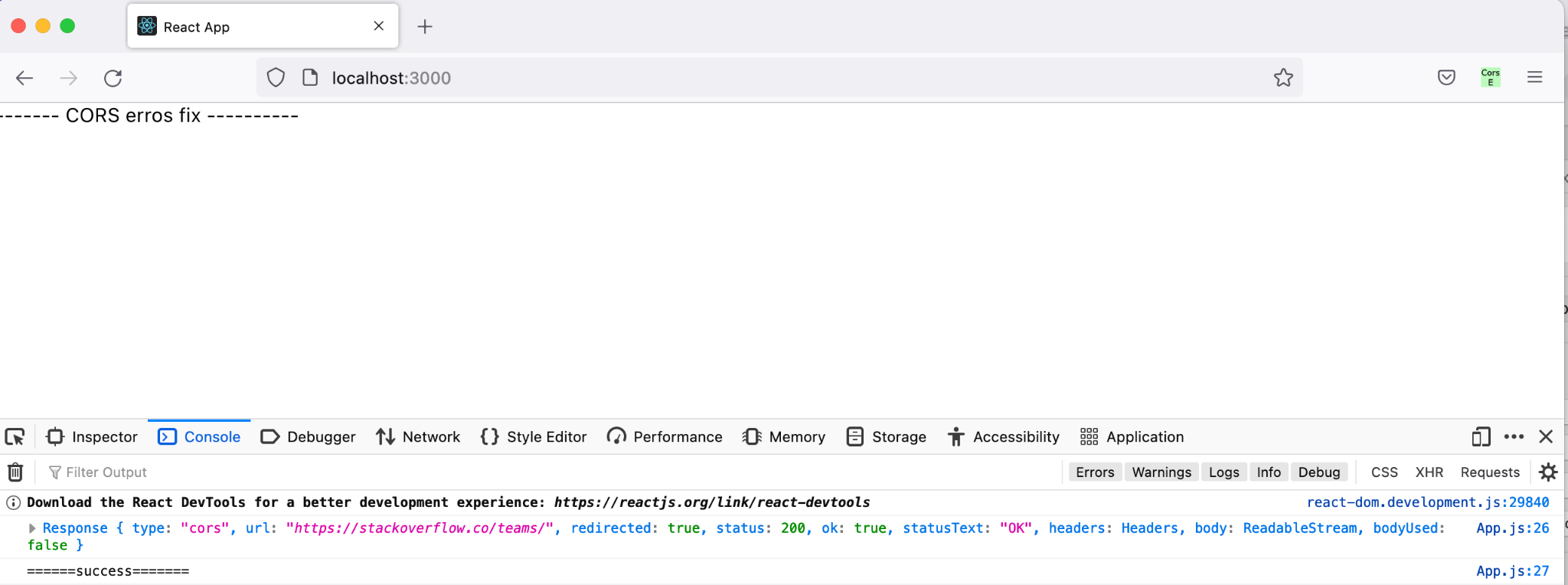
Before and after enabling CORS Everywhere extension in Firefox
Safari
- Enable the develop menu by going to Preferences > Advanced.
- Then select “Disable Cross-Origin Restrictions” from the develop menu.
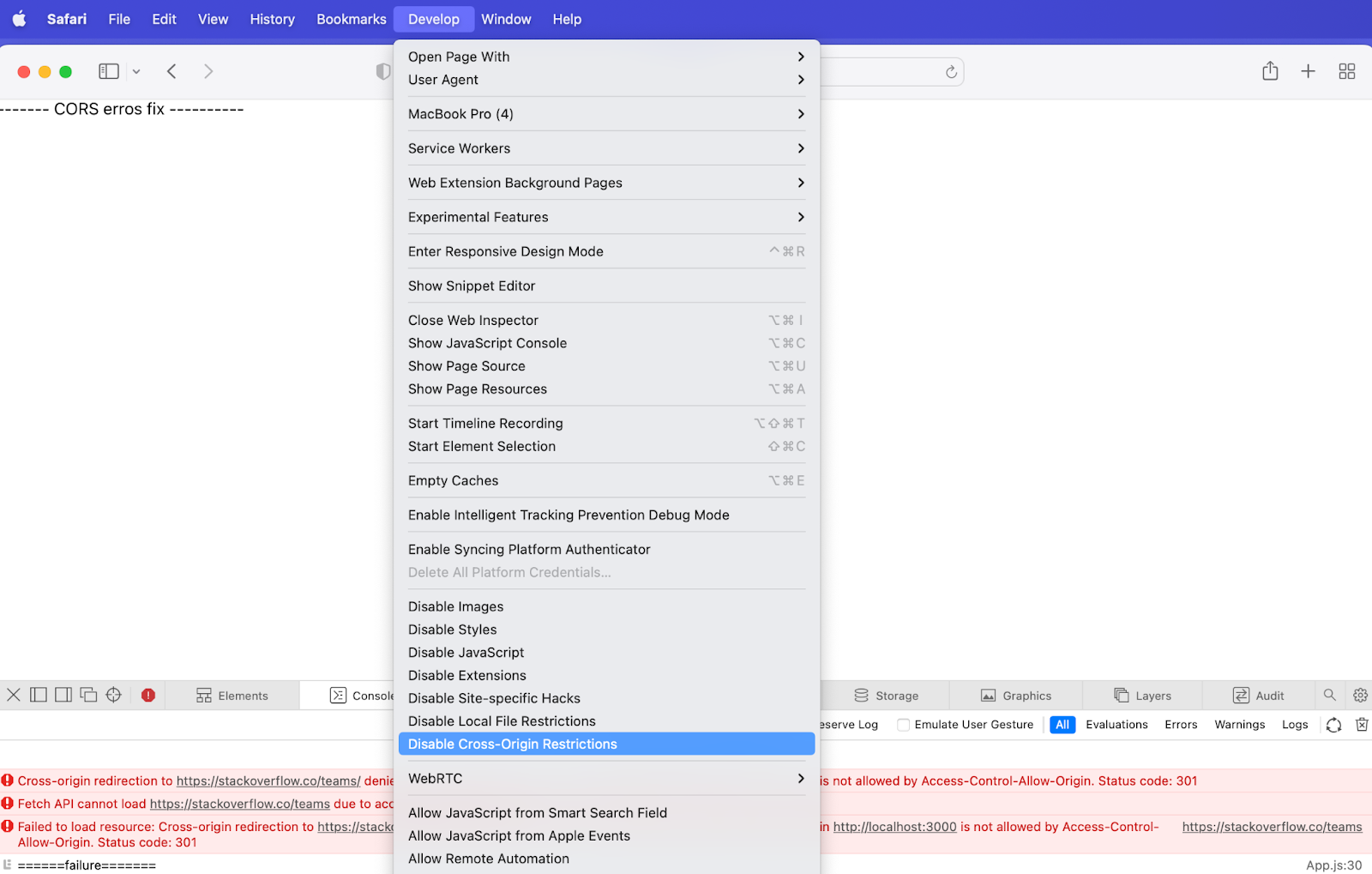
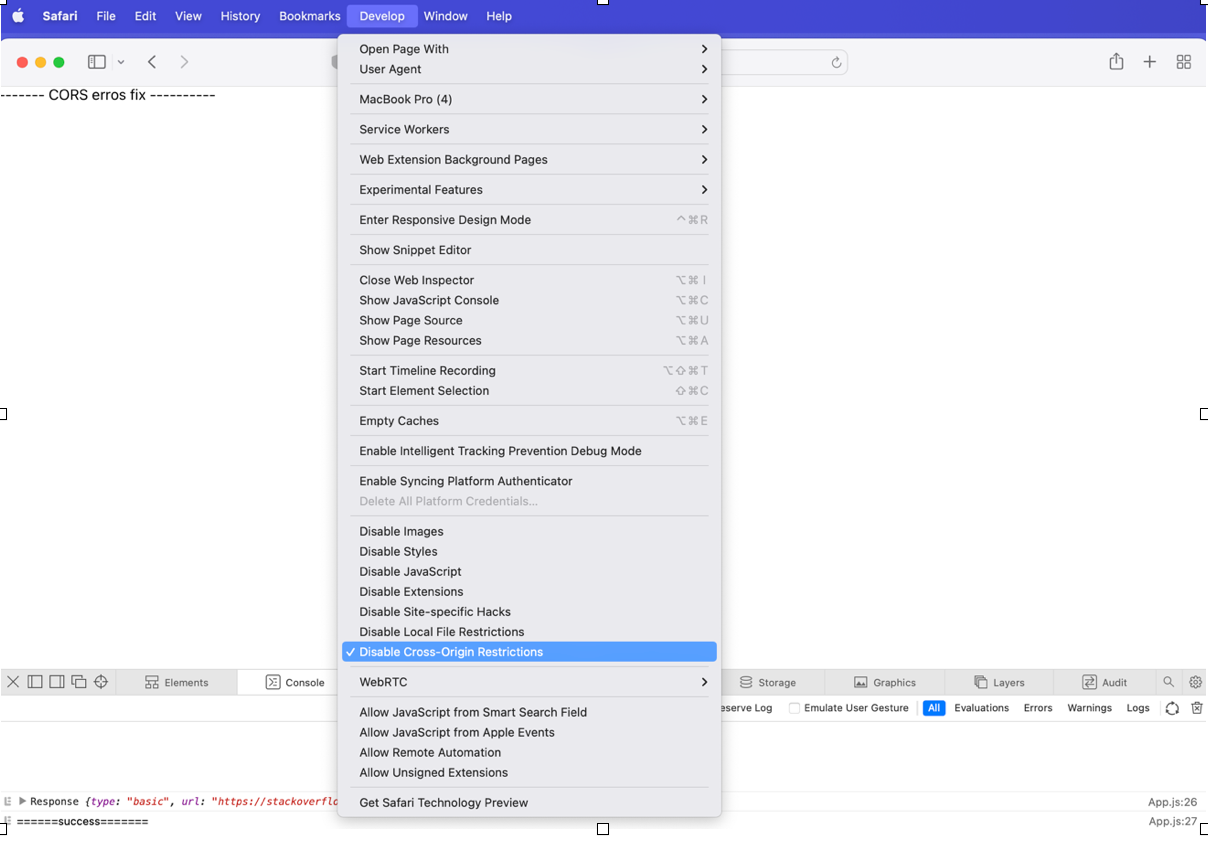
Before and after checking ‘Disable Cross-Origin Restrictions’ in Safari
Enable CORS on server side:
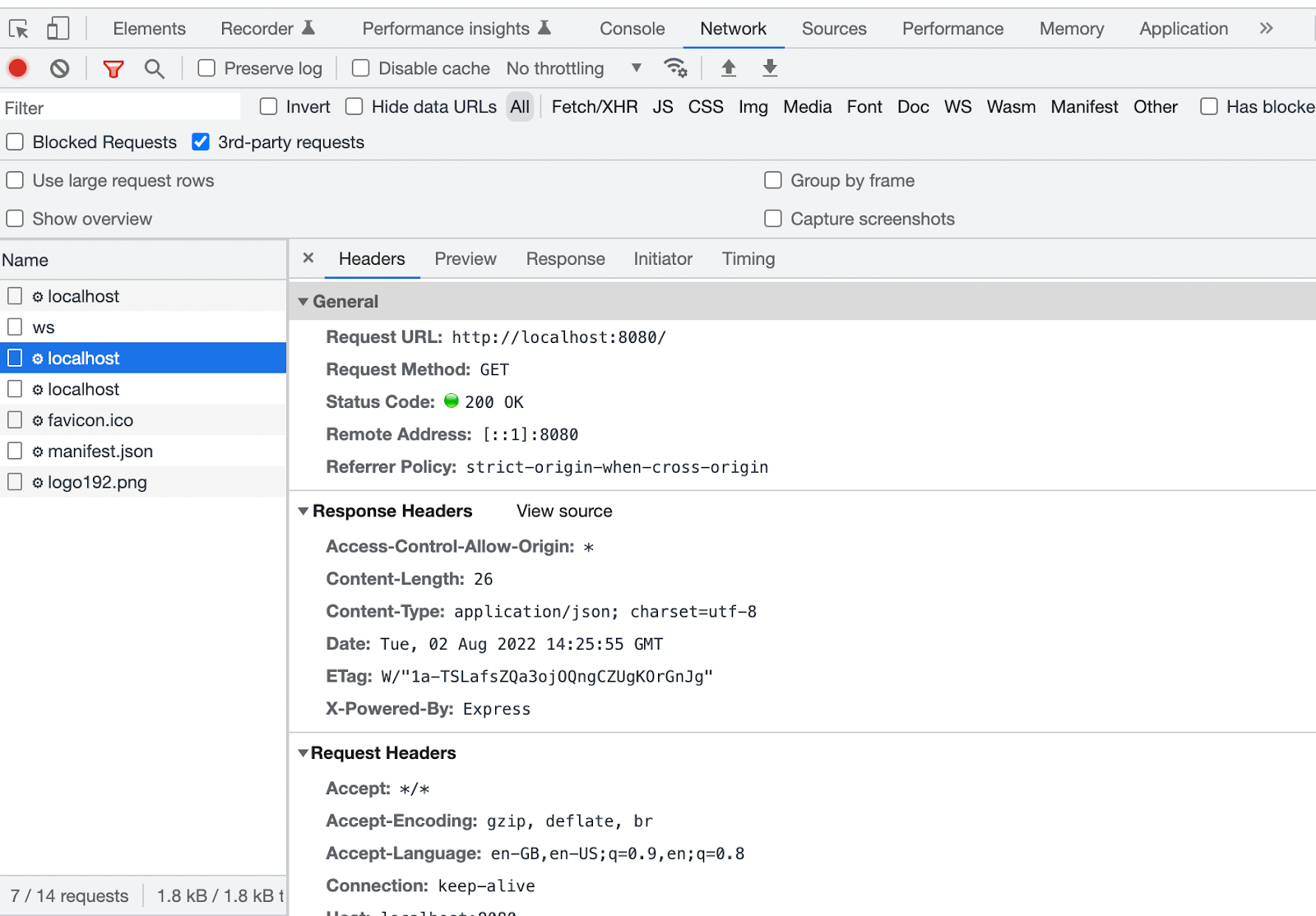
If we see the CORS error in the attachment below it states that there is a missing ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ on the resource you requested.

Actually, the client doesn’t have to do anything with CORS error, it is something that the browser imposes and it is suggested that requested resources should be configured differently. Hence, at first place CORS error should preferably be handled from server side.
- To do so add res.set(‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’, ‘*’);
In our server’s request function ‘*’ indicates that resources can be requested by any client. - You can also set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin to specific domains instead of the asterisk. For instance, setting it to http://localhost:3000 will only enable CORS for clients that are running on the specified URL, localhost:3000. i.e. res.set(‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’, ‘http://localhost:3000’);
- To illustrate how CORS errors can be fixed on the server side, let’s create a simple server using Express with some API endpoints.
1. First to create a folder you can run following command in terminal:
1mkdir my-server && cd my-server
This should create an empty folder ‘my-server’.
2. Now initialize a new npm project inside it by running:
1npm init -y
A package.json file should be created inside your project.
3. Let’s install Express.js by running following command in terminal:
1npm i express
4. Next create an app.js file in the root directory, which will be the entry point of our application and add the code below. This server listens on port 8080 and has two routes, the ‘/‘ and ‘/cors’ that sends responses.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11const express = require('express'); const app = express(); const PORT = process.env.PORT || 8080; app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.send({ "msg": "This is homepage" }) }) app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log('Server is running on port 8080’) })
5. Lets run our server using command:
1node app
localhost:8080 should be running as in attachment below -

6. Replace code in App.js file of your React app as below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22import { useEffect } from 'react'; function App() { const makeAPICall = async () => { try { const response = await fetch('http://localhost:8080/'); const data = await response.json(); console.log({ data }) } catch (e) { console.log(e) } } useEffect(() => { makeAPICall(); }, []) return ( <div className="App"> <h1>------- CORS erros fix ----------</h1> </div> ); } export default App;
In the above code, we make an api call to ‘http://localhost:8080/" in the makeAPICall function which is called when the component is mounted. On npm start, if we check our browser’s console we should see a CORS error as in the attachment below -
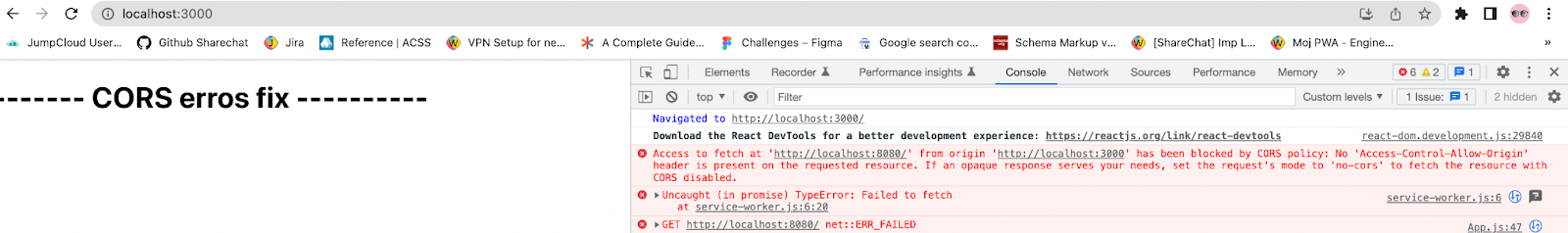
The above is the typical CORS error that occurs because your browser is blocking requests to your server. Even though both your client and the server are running from localhost, your server is hosted on port 8080 and your React client on port 3000. Therefore, both have a different origin, and the browser's SOP policy comes into play.
7. To fix CORS error on server side: Update server’s app.js by adding res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', ‘*'); in the code as below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12const express = require('express'); const app = express(); const PORT = process.env.PORT || 8080; app.get('/', (req, res) => { res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*'); res.send({ "msg": "This is homepage" }) }) app.listen(PORT, () => { console.log('Server is running on port 8080’) })
8. Restart the server and now since the resource can be requested by any client CORS error should be fixed as in attachment below.
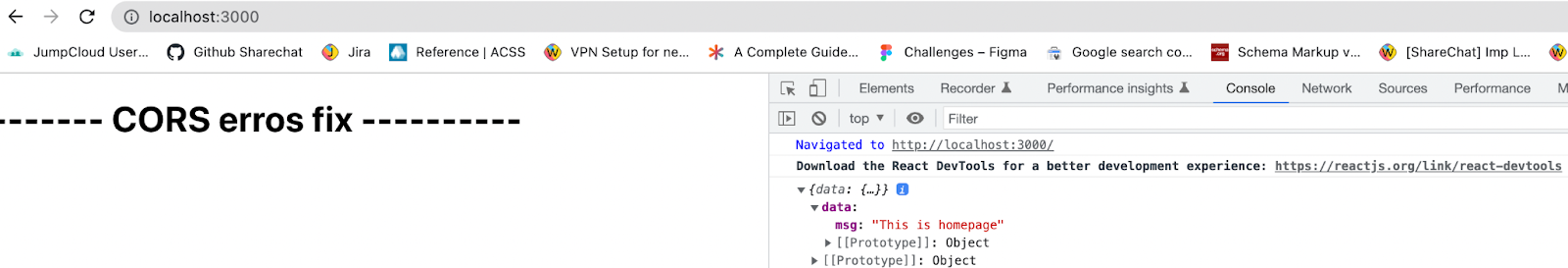
Conclusion
CORS errors can be a pain to front-end developers. But these fixes above can definitely speed up the development process without getting blocked by these errors.
We are hiring!
At ShareChat, we believe in keeping our Bharat users entertained in their language of preference. We are revolutionizing how India consumes content and the best in class Engineering technology is at the forefront of this transformation. In addition, you'll also get the opportunity to work on some of the most complex problems at scale while creating an impact on the broader content creation ecosystem.
Exciting? You can check out various open roles here!
Illustrations - Haritha NV.



